近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授与河南师范大学冯精兰教授联合团队在新污染物液晶单体分析检测技术方面取得最新研究进展,研究成果以《Optimization, validation, and implementation of a new method for detecting liquid crystal monomers in dust using GC− MS/MS with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization》为题发表在Analytica Chimica Acta 2025, 1354, 344002期刊(https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2025.344002)上。论文的第一作者为博士生韩静,通讯作者为河南师范大学冯精兰教授和安太成教授。本研究开发并优化了一种基于大气压化学电离源的气相色谱-串联质谱法,用于检测灰尘中的液晶单体。该方法为深入研究液晶单体的分布特征、来源解析及其迁移转化行为提供了重要的技术支持。

论文DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2025.344002
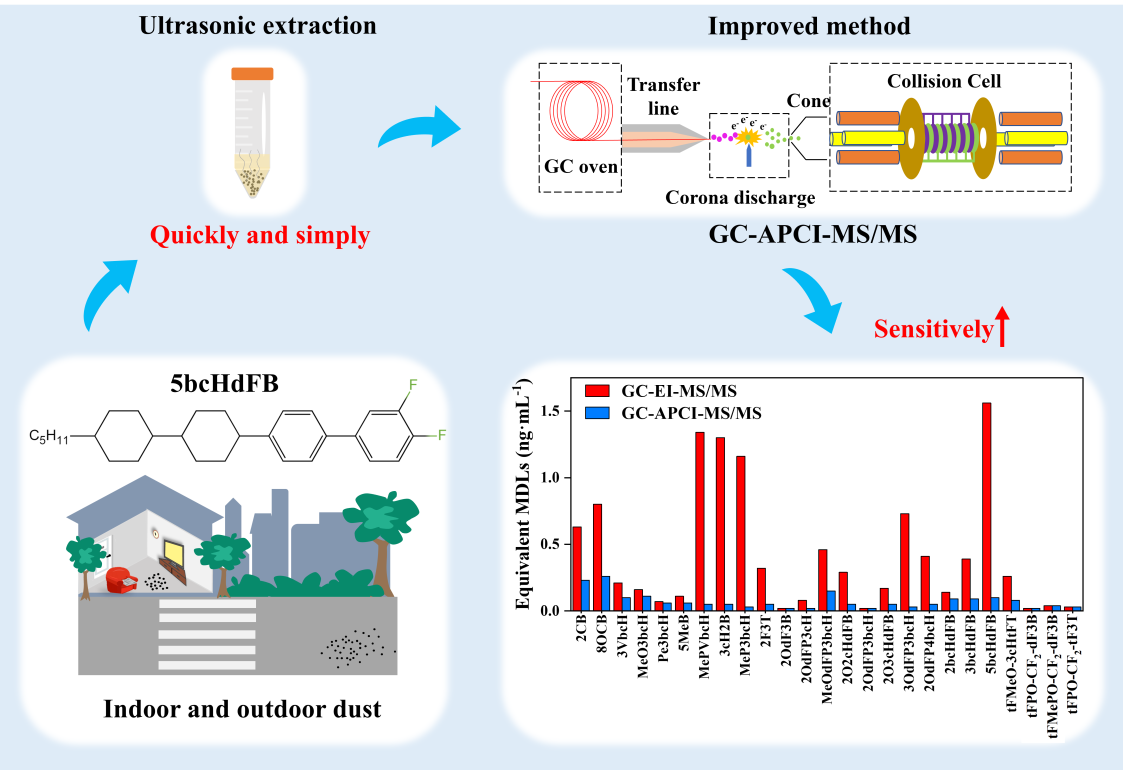
本研究开发了一种改进的大气压化学电离源的气相色谱-串联质谱法,用于同时分析26种液晶单体,并验证了其在灰尘样品中检测液晶单体的有效性。在最佳仪器条件下,该方法对液晶单体的IQL低至 0.02 pg·进样-1,能够实现对灰尘样品中低至0.02 ng·g-1浓度水平的 LCMs 的精准测定。与EI条件下获得的结果相比,该方法显著降低了LCMs 的方法检出限(MDL)。基质空白样品中低、中、高浓度加标样品的回收率范围为 54.8 % 至 117 %,相对标准偏差(RSD)低于16 %,表明方法具有良好的准确性和精密度。在室内灰尘样品中共鉴定出7种 LCMs,其中氟代液晶单体(F-LCM)的含量显著高于非氟代液晶单体(n-LCM)。相比之下,在室外灰尘样品中仅检测到一种F-LCM。上述结果充分证实了所开发方法的可靠性、精密度和适用性。尤为重要的是,该改进方法不仅适用于灰尘样品的分析,还可扩展至其他类型环境样品的检测,为深入研究痕量 LCMs 在环境中的分布特征、迁移行为及来源解析提供了重要技术支持。
图文摘要:
论文的英文摘要附如下:
ABSTRACT:
Background
Liquid crystal monomers (LCMs) are a new class of emerging pollutants. To assess their occurrence, behaviour, and potential risks, a sensitive and selective analytical method is required for the determination of LCMs at trace levels in multiple environmental media. Toward this end, an improved GC−MS/MS method was developed and validated for the quantification of LCMs.
Results
The method integrates atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (APCI) with GC−MS/MS. Under optimal instrumental conditions, the instrument quantification limits of LCMs reached as low as 0.02 pg·injection-1, which can be attributed to the generation of high-abundance molecular ions/quasi-molecular ions under APCI. Compared to previously published methods, the developed method in this study reduces the method detection limits of LCMs by approximately 1−38.7 times, enabling the analysis of LCMs at concentrations as low as 0.02 ng·g-1 in dust samples. This improved approach was applied to both indoor and outdoor dust samples. The concentrations of LCMs obtained in this study are consistent with those reported in previous research, demonstrating high detection frequencies of fluorinated LCMs and their predominance in dust.
Significance
The developed method in this study is not only applicable to dust samples but also readily extends to other environmental matrices, thereby facilitating the investigation of the occurrence, origin, and migration of LCMs in various environments.
项目致谢:本研究得到国家自然科学基金(41771511)的大力支持。