
近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队在催化降解环烷烃方面取得最新研究进展,研究成果以《Efficient Catalytic Combustion of Cyclohexane over PdAg/Fe2O3 Catalysts under Low-Temperature Conditions: Establishing the Degradation Mechanism using PTR-TOF-MS and in situ DRIFTS》为题发表在ACS Applied Materials Interfaces, 2022, 14(50), 55503–55516 (https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c14515)期刊上。论文的第一作者为博士生刘秋霞,通讯作者为安太成教授。该工作重点针对危害环境健康且低温难于降解的环烷烃,并以环己烷为例构建了具有低温催化氧化能力的PdAg/Fe2O3纳米催化剂。研究比较了PdAg/Fe2O3、Pd/Fe2O3、Ag/Fe2O3和Fe2O3对环己烷的热催化氧化性能及其稳定性。用XRD、TEM、XPS、H2-TPR、NH3-TPR等研究PdAg合金、氧空位和Fe2O3的构效关系,探究了PdAg/Fe2O3对环己烷表现出优异的催化性能的原因。再通过in situ DRIFTS和PTR QMS分别对其催化氧化过程中催化剂表面和尾气中的中间副产物进行鉴定,推导出了环己烷在PdAg/Fe2O3纳米催化剂上的反应路径和催化氧化机理。这项深入研究将有助于设计和应用高效催化剂以在低温下有效燃烧VOCs。
论文的网址:https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c14515
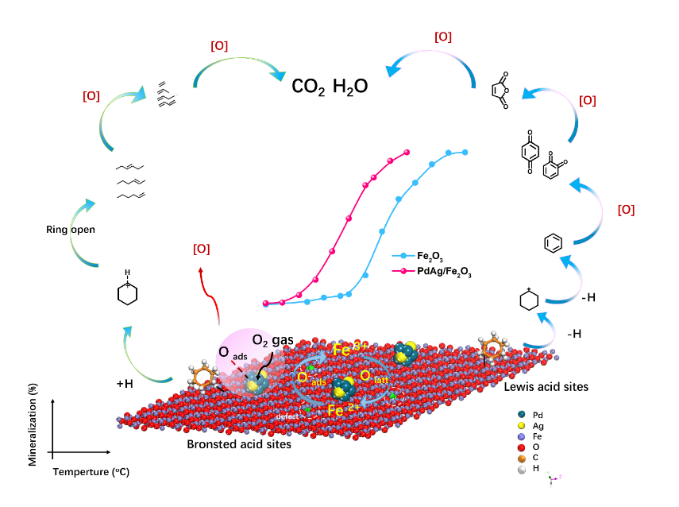
环己烷是一种典型的挥发性有机化合物(VOC),对环境具有一定的风险。在此,我们合成的PdAg/Fe2O3催化剂在较低的温度(50%矿化温度(T50):199 ℃,90%矿化温度(T90):315 ℃)下对环己烷燃烧表现出优异的催化性能,而Pd/Fe2O3(T50:262℃,T90:335℃)和Fe2O3(T50:305℃,T90:360℃)。此外,PdAg/Fe2O3通过AgPd合金负载增强Fe2O3的低温还原性和酸性强度,从而表现出增强的催化性能和稳定性。原位漫反射红外傅里叶变换光谱和质子转移反应飞行时间质谱分别用于识别氧化过程中催化剂表面和尾气中形成的中间体。结果表明:将PdAg负载到Fe2O3上显著增强了氧和环己烷的吸附和活化、环己烷氧化脱氢制苯以及环己烷在低温下催化裂化制烯烃。这项研究将有助于设计和应用高效催化剂在低温下有效实现的VOCs热催化燃烧。
图文摘要:
英文摘要:
Cyclohexane, a typical volatile organic compound (VOC), poses high risks to the environment and humans. Herein, synthesized PdAg/Fe2O3 catalysts exhibited exceptional catalytic performance for cyclohexane combustion at lower temperatures (50% mineralization temperature (T50) of 199 oC, 90% mineralization temperature (T90) of 315 oC) than Pd/Fe2O3 (T50 of 262 oC, T90 of 335 oC) and Fe2O3 (T50 of 305 oC, T90 of 360 oC). In addition, PdAg/Fe2O3 displayed enhanced catalytic performance and stability, due to the low-temperature reducibility and the acidity of PdAg/Fe2O3 were enhanced by the PdAg alloy. In situ diffuse reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy and proton-transfer-reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry were applied to identify the intermediates formed on the catalyst surface and in the tail gas during oxidation, respectively. Results suggested that loading PdAg onto Fe2O3 significantly enhanced the adsorption and activation of oxygen and cyclohexane, oxidative dehydrogenation of cyclohexane to benzene, and catalytic cracking of cyclohexane to olefins at low temperatures. This in-depth study will benefit the design and application of efficient catalysts for the effective combustion of VOCs at low temperatures.
资助项目:本研究得到广东省重点领域研发计划项目(2019B110206002)、广东省创新科研团队(2017BT01Z032)和国家自然科学基金(42020104001,42007192和42077332)的支持。