近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队题为《Preferential removal of aromatics-dominated electronic industrial emissions using the integration of spray tower and photocatalysis technologies》的学术论文在国际期刊Journal of Cleaner Production(2022, 364:132706)杂志上发表(ttps://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.132706),论文第一作者为硕士生张晓龙,通讯作者为安太成教授。

论文网址:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0959652622023046
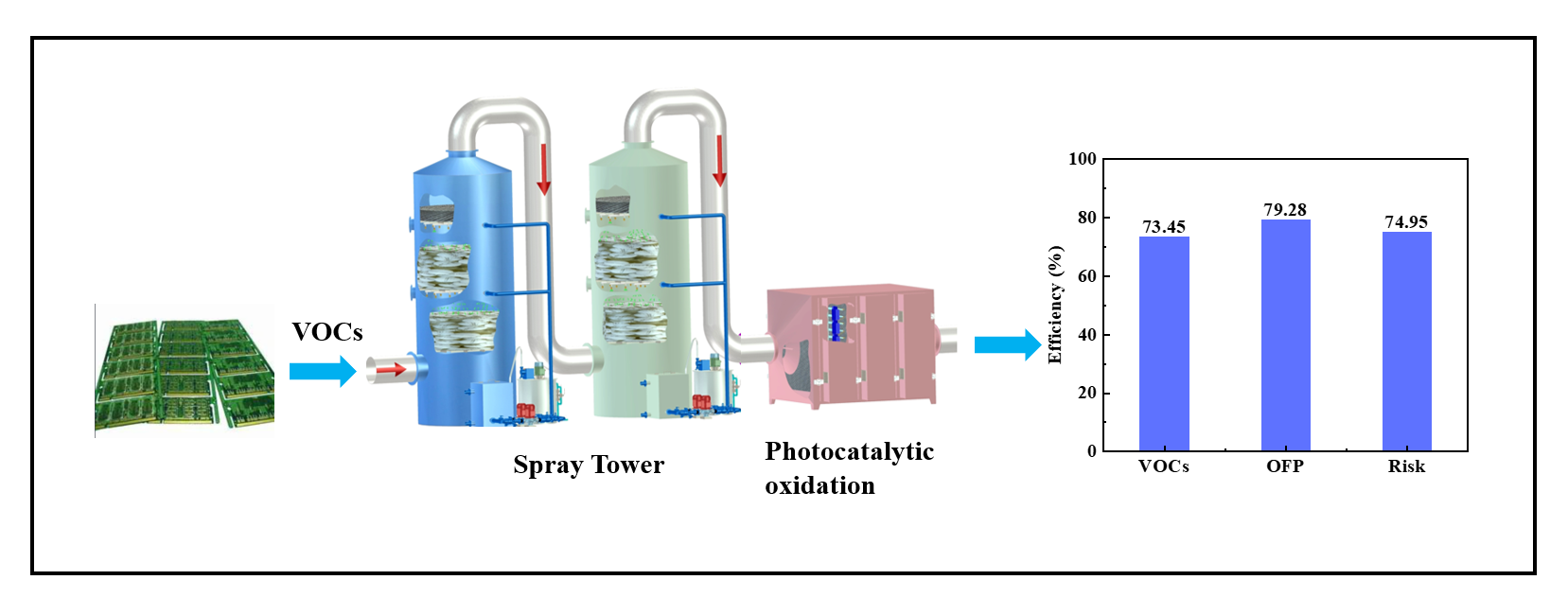
电子产品的制造过程中,会排放大量有毒有害的挥发性有机化合物(VOCs),对环境和人体健康造成严重危害,因此研发高效稳定污染控制技术具有非常重要的社会和环境意义。本研究首先分析了PCB生产过程产生有机废气排放特征,发现PCB生产过程中共产生66种VOCs,总挥发性有机化合物(TVOCs)平均浓度达到23.35 mg/m3,其中芳香类化合物(AHs)占总浓度的88.36%。根据电子行业排放以芳香烃为主的有机废气,选择了以喷淋加光催化为主的组合治理工艺。通过对组合工艺为期270天的性能跟踪发现组合工艺对废气中TVOCs的平均去除效果达73.60 %,其中喷淋对TVOCs的平均处理效率为18.40%,光催化单元的去除效率为55.20%,特别是光催化工艺对(AHs)表现出最高选择性去除效果(61.30%)。臭氧生成潜势评估结果显示,组合工艺对臭氧生成潜势消减效果为79.28 %,同时致癌与非致癌健康风险显著下降。该研究对光催化技术应用于治理大风量低浓度工业有机废气具有一定的理论意义和实用价值。
图文摘要
论文的英文摘要附如下:
ABSTRACT:
Printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing industrial emission, characterized with low concentration and high gas flow rates, is one of the important sources of toxic and odorous volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are deleterious to human health and severed as important precursors for ozone formation. Here, we conducted a case study in which an integrated decontamination technique of spray tower (ST) with photocatalysis (PC) was applied to purify the waste gas emitted from a PCB manufacturer. Total 66 VOCs including halogenated hydrocarbons (HHs), aromatic hydrocarbons (AHs), oxygen-containing hydrocarbons (OVOCs), and aliphatic hydrocarbons (AIHs) were quantified using GC-MS during four sampling events. AHs were the largest groups (contributing 88.36 % of the sum of VOCs). The average removal efficiency (RE) of VOCs during the nine months continuous treatment was 73.60%. High RE can be attributed to the following three aspects: the capture efficiency of HHs with slight water solubility (50.16% of RE) and AIHs with low saturated vapor pressure (54.75% of RE) was improved by ST before PC, and AHs was preferentially degraded by PC (61.34% of RE). In addition, ozone formation potentials and health risk (cancer and non-cancer risks) greatly decreased after ST-PC treatment. This study suggests that ST-PC technique is a promising approach for removal of continuous exhausted organic waste gas with low concentration and high gas flow rates, as well asreducingozone formation and health risk.