近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院在环境科学与工程领域顶级期刊Environmental Science & Technology(IF=9.028)上发表题为《Oxygen Isotope Tracing Study to Directly Reveal the Role of O2 and H2O in the Photocatalytic Oxidation Mechanism of Gaseous Monoaromatics》的学术论文。

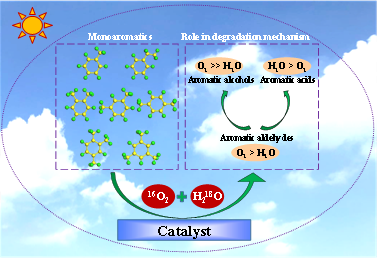
众所周知,O2和H2O会影响气态芳香烃的光催化氧化机理,但由于缺乏直接证据,目前的影响机制尚不清楚。通过追踪氧原子从16O2和H218O到中间产物可以阐明上述作用机制。研究发现:当H218O含量低时可以抑制二甲苯氧化过程中对苯二甲醛的形成,而16O2对总产物的生成影响很大,但H218O和16O2均不会影响产物的浓度百分比顺序。同位素结果表明甲基苯甲醛、甲基苯甲醇和对苯二甲醛的氧原子中16O占主导(≥69.49%),而甲基苯甲酸和苯酞的氧原子中18O分布较高(≥59.51%)。结合产物的相互转化结果发现,16O2导致二甲苯首先转化为甲基苯甲醛,然后转化为甲基苯甲醇或对苯二甲醛,而H218O对于甲基苯甲醛转化为甲基苯甲酸或苯酞的贡献更大。分子动力学计算进一步证实了二甲苯及其产物与H2O和O2的相互作用位点。此外,16O2和H218O在降解甲苯、乙苯、1,2,4-三甲苯和1,3,5-三甲苯中也起到了在二甲苯中相同的作用。本研究首次提供了O2和H2O在气态芳香烃光催化氧化机制中作用的直接证据,研究结果有助于实现芳香烃降解产物的可控生成,并预测芳香烃在大气环境中的迁移过程。
Graphical Abstract
论文链接: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.1c05134
论文英文摘要:
O2 and H2O influence photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of gaseous monoaromatics, but still in unclear manner, due to lack of direct evidence. Tracing oxygen atom from 16O2 and H218O to intermediate can clarify their roles. Low H218O content suppressed formation of benzenedicarboxaldehydes during oxidation of xylenes and 16O2 more affected yield of total intermediates, while neither of them altered amount percentage order of products. Methylbenzaldehydes, methylbenzyl alcohols and benzenedicarboxaldehydes possessed dominant 16O percentage (≥69.49%), while higher 18O distribution was observed in methylbenzoic acids and phthalide (≥59.51%). Together with interconversion results of products revealed 16O2 determining transformation of xylenes initially to methylbenzaldehydes and then to methylbenzyl alcohols or benzenedicarboxaldehydes, while H218O mainly contributed for conversion of methylbenzaldehydes to methylbenzoic acids or phthalide. Further interaction sites of xylene and its product with H2O and O2 were confirmed by molecular dynamic calculations. Same roles of 16O2 and H218O in degradation of toluene, ethylbenzene, 1,2,4-trimethylbenzene and 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene were also verified. This is the first time to provide the direct evidence to reveal role of O2 and H2O in photocatalytic oxidation mechanism of gaseous monoaromatics. The findings are helpful to achieve controllable product formation from oxidation of monoaromatics and predict their migration process in atmospheric environment.