近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院硕士生刘淑慧、博士生景冰花和敖志敏教授等在MoS2纳米花压电催化活化过硫酸盐降解水中有机污染物的研究方面取得新的研究进展,研究成果以“Piezoelectric Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by MoS2 Nanoflowers for Enhanced Degradation of Aqueous Organic Pollutants”为题发表在《Environmental Science: Nano》上。

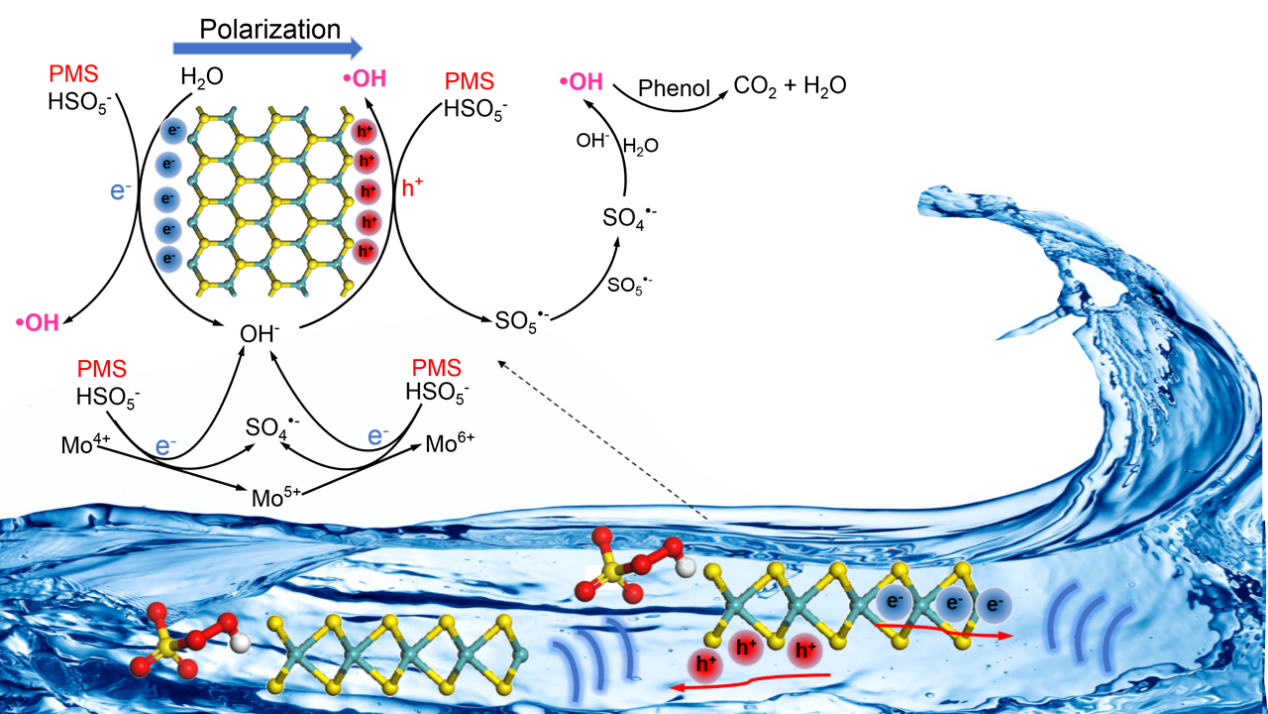
目前,基于过硫酸盐的高级氧化法受到大家的广泛关注,探索节能和高性能的方法来活化过硫酸盐以净化有机物,对高级氧化法处理废水具有重要的意义。压电效应作为一种物理现象,由于外部机械振动导致结构形变,从而引起压电材料自发极化,形成内置电场,已广泛应用在纳米发电机和自发电系统中。近年来,压电效应还可以通过压电催化作用来驱动化学反应,例如水分解和有机污染物的降解。与传统的压电材料相比,二维(2D)压电材料具有更高的结晶度和更大的弹性形变耐受力,因此受到了人们的广泛关注。但是,这些2D压电晶体在基于过硫酸盐高级氧化(PS-AOP)中的应用几乎没有被探索过。二维压电材料压电催化活化过硫酸盐过程中所涉及的催化机理和反应途径尚不确定。特别是,目前我们仍然缺乏对2D材料的压电行为的基本了解,并且压电诱导的载体和过硫酸盐之间的氧化还原反应诱导的ROS的演化也不明确。因此,本文采用二硫化钼纳米花(MoS2NFs)作为模型2D压电催化剂,以激活过一硫酸盐PMS降解苯酚。通过实验和密度泛函理论(DFT)计算,研究了2D压电材料催化PMS活化过程的内在机理。通过淬灭实验和电子顺磁共振(EPR)技术,在压电催化PMS活化过程中确定了基于自由基的反应途径。进行了DFT计算以阐明MoS2纳米片的压电极化与原子取向之间的相关性,超声(US)振动引起的不同应变下的极化MoS2纳米片中的电荷分布以及PMS与MoS2边缘上的电荷载流子之间的相互作用产生的活性氧物种。这项工作不仅加深对2D材料和压电催化高级氧化法的理解,也为压电激活过硫酸盐以降解水中有毒有机污染物提供了一种的有效方法和思路。
论文网址:https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN01237H
图表摘要:
论文英文摘要:
Natural mechanical energies, such as wind, tide waves, and water flow, are widely existed in the environment and these inexhaustible natural mechanical energies can be utilized through piezoelectric materials for the degradation of aqueous organic pollutants in the environment. In this work, few-layered molybdenum disulfide nanoflowers (MoS2 NFs) were adopted as a piezocatalyst to activate peroxymonosulfate (PMS) with ultrasonic wave (US) as the mechanical force for phenol abatement. A much higher degradation efficiency was attained by the integrated US/MoS2NFs/PMS system compared to the other single systems, revealing the markedly synergistic effect of US and MoS2on PMS activation. Moreover, density functional theory calculations were performed to fundamentally understand the charge distribution in a polarized MoS2nanosheet under different strains to understand the piezocatalytic properties of the MoS2nanosheets, as well as the reaction pathways between PMS and carriers on the active edges of MoS2 for free radical production. It was found that both sulfate radicals (SO4•‒) and hydroxyl radicals (•OH) were produced in the US/MoS2NFs/PMS system. However, SO4•‒was quickly converted into •OH via the hydrolysis reaction under US, enabling •OH to be the primary reactive oxygen species for phenol oxidation. This work offers an efficient piezocatalyst to activate persulfate for water remediation. More importantly, it provides fundamental insights into the piezoelectricity in two-dimensional semiconducting materials and the mechanism in piezocatalytic activation of persulfate. The results prove that the combination of piezoelectricity and advanced oxidation processes is promising for water pollution control, and provides a new idea for the application of inexhaustible natural mechanical energy in the environment for environmental remediation.
资助项目:
本研究受到国家自然科学基金(21806024和21777033),中国博士后科学基金(2017M622637),广东省科学技术计划项目(2017B020216003),广东省自然科学基金(2020A1515011150)及广东省教育厅创新团队项目(2017KCXTD012)的支持。