近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院安太成教授团队题目为《New Mixed Bromine/Chlorine Transformation Products of Tetrabromobisphenol A: Synthesis and Identification in Dust Samples from an E‑Waste Dismantling Site》的学术论文在Environmental Science & Technology(ES&T)杂志上发表。ES&T杂志是环境科学与工程学科的一区杂志,在环境科学与技术领域中具有非常重要的影响。论文的第一作者为广东工业大学-西北师范大学联合培养硕士研究生刘晶和广东工业大学马盛韬博士,通讯作者为西北师范大学张彰副教授和广东工业大学余应新教授。

该工作采用了多种色谱质谱分离技术,结合有机合成的手段,对电子垃圾拆解车间灰尘样品提取物中多种TBBPA脱溴及混合溴/氯转化产物进行了筛查与鉴定,通过合成转化产物标准品并进行色谱共注分析,对电子垃圾灰尘样中的多种TBBPA转化产物进行了确证。研究结果表明,在复杂的电子垃圾拆解处置过程中,TBBPA可以发生氯化形成溴/氯混合卤代转化产物,这一研究为深入理解TBBPA引发的环境问题提供必要的理论指导。
Graphical Abstarct
论文DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.0c04494
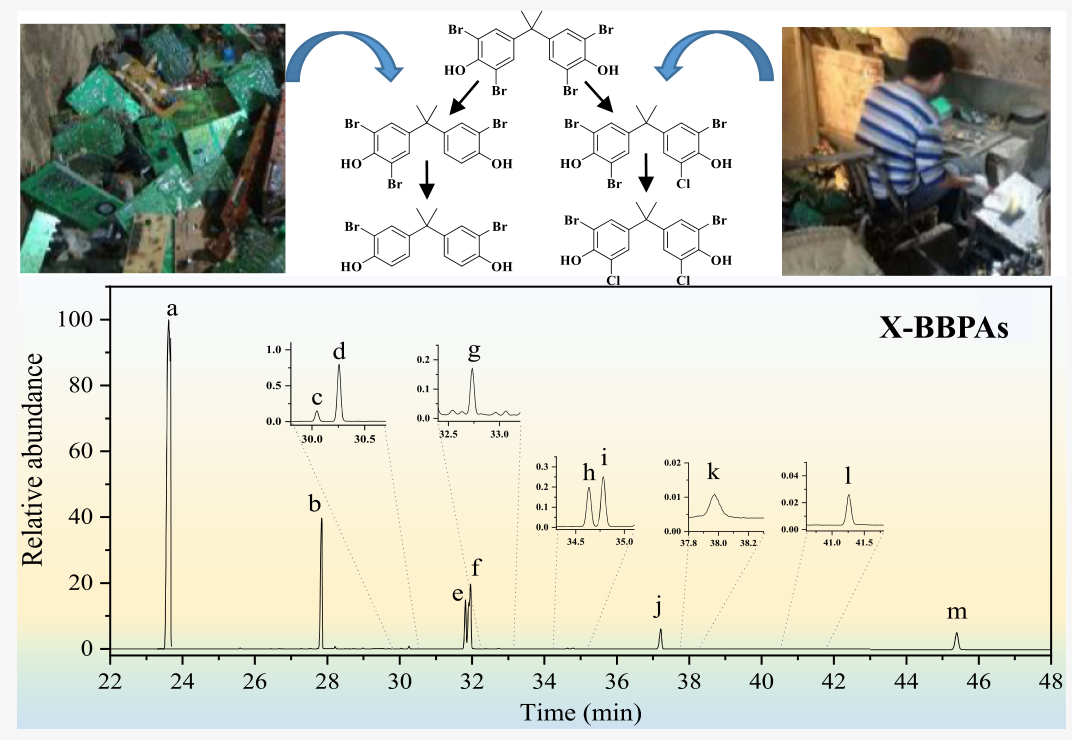
四溴双酚A(TBBPA)及其衍生产品作为最普遍使用的阻燃剂,其大规模生产和使用造成了广泛的环境污染,并引发了人们对其潜在的内分泌干扰效应及对人类和生态系统影响的关注。在本研究中,从电子垃圾拆解车间灰尘样品中筛选出了TBBPA的脱溴以及未知的溴/氯混合转化产物(X-BBPA)。通过合成五种一氯产物(2-氯-2',6,6'-TriBBPA,2-氯-2',6-DiBBPA,2-氯-2',6'- DiBBPA,2-氯-2'-MoBBPA,和2-氯-6-MoBBPA)和两种二氯产物(2,2'-二氯-6,6'DiBBPA和2,2'-二氯-6-MoBBPA),对比未知TBBPA转化产物与合成标准品的质谱特征和保留时间,对未知物进行了结构鉴定。研究显示,电子废物拆解车间灰尘样品中X-BBPA的平均浓度为1.63×104 ng/g,其浓度水平与TBBPA相似;但是,X-BBPA浓度比TBBPA脱溴产物低了一个数量级。因此,脱溴和氯-溴置换反应都可能是电子垃圾处理过程中的重要反应。TBBPA化合物结构简单,可以成为理解卤代化合物的溴/氯交换反应的理想模型化合物。电子垃圾拆解灰尘样品中检出了较高水平的TBBPA转化产物,这表明今后更多的研究中应该针对这些产物,弄清TBBPA转化产物的形成和排放,以及它们的暴露对于电子垃圾拆解从业工人的潜在健康影响。
论文英文摘要附如下:
ABSTRACT: The large-scale production and usage of tetrabromobisphenol A (TBBPA) and its analogues have caused widespread contamination, raising concern about their potential endocrine disruption effects on both humans and ecosystems. In the present study, debromination and unknown mixed bromine/chlorine transformation products of TBBPA (X-BBPA) were screened in dust samples from an e-waste dismantling site. Five monochloro products (2-chloro-2′,6,6′-TriBBPA, 2-chloro-2′,6-DiBBPA, 2-chloro-2′,6′- DiBBPA, 2-chloro-2′-MoBBPA, and 2-chloro-6-MoBBPA) and two dichloro products (2,2′-dichloro-6,6′-DiBBPA and 2,2′-dichloro-6-MoBBPA) were successfully synthesized and structurally identified. TBBPA and its transformation products were detected by comparison of their mass spectra and retention times with those of synthetic standards. The mean concentration of X-BBPA was 1.63 × 104ng/g in e-waste dismantling workshop dust samples based on dry weight, which was at a similar level to TBBPA. However, it was order of magnitude lower than the concentrations of the debromination congeners. Thus, both debromination and chlorinebromine exchange may be important reactions during the thermal processing of e-waste. The results on mixed chlorinated/brominated TBBPA transformation products provided new insights into TBBPA transformation. The elevated levels of the transformation products of TBBPA suggested that these products should be targeted to avoid underestimation of possible health risks.