近日,广东工业大学环境健康与污染控制研究院、环境科学与工程学院聂纯阳博士后、研究生戴振华和敖志敏教授等在非金属纳米碳催化剂/过硫酸盐高级氧化体系的非自由基氧化机理及其在水处理中的应用方面取得最新的研究进展,研究成果以 “Criteria of active sites in nonradical persulfate activation process from integrated experimental and theoretical investigations: boron-nitrogen-co-doped nanocarbons mediated peroxydisulfate activation as an example” 为题发表在《Environmental Science: Nano, 2020, 7: 1899》上,并入选封面文章和热点文章。

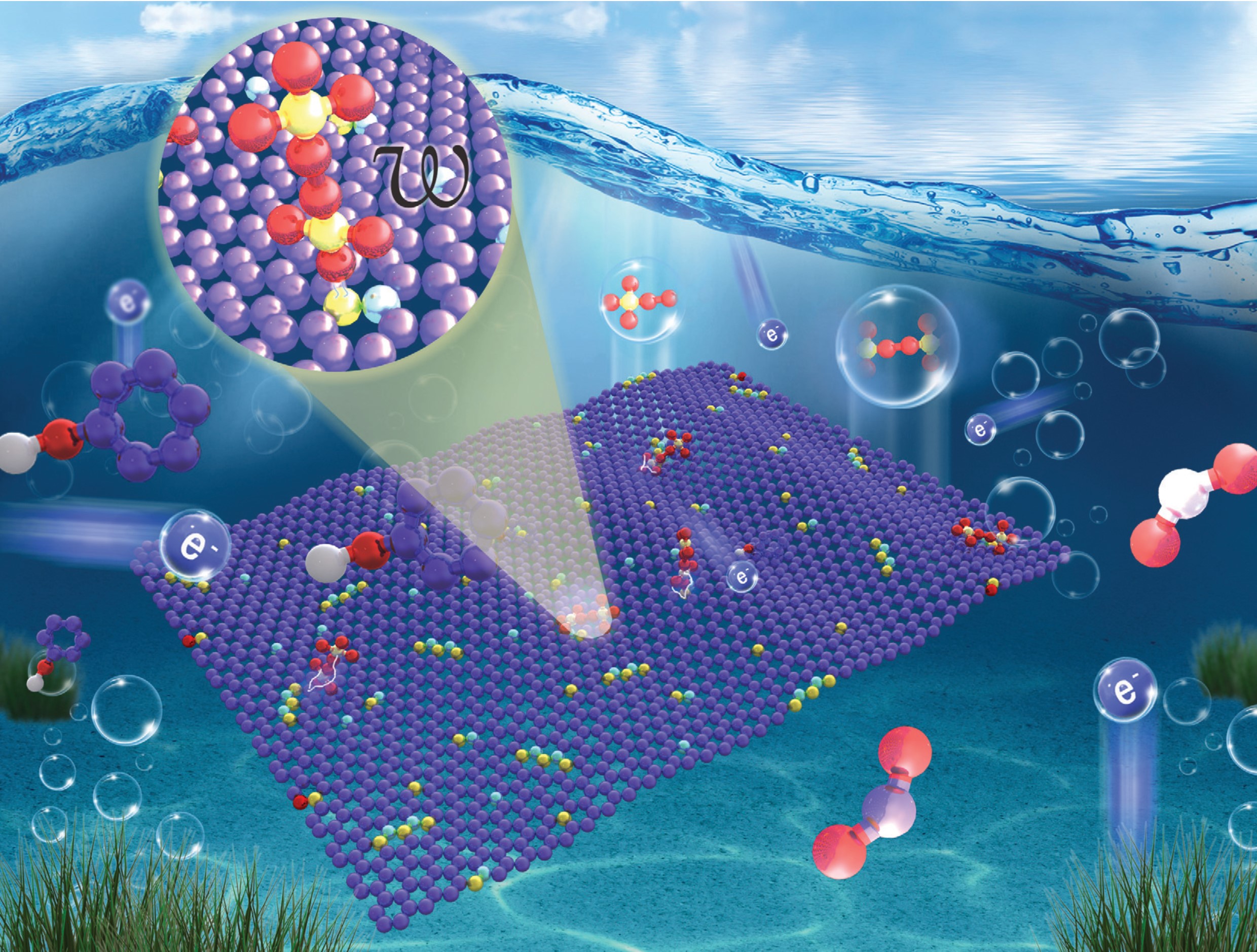
碳催化剂/过硫酸盐(PDS)体系是一种新型的非金属高级氧化体系,能有效去除水中的污染物。近年来,基于电荷转移机理为主的过硫酸盐活化过程由于其神秘的非自由基氧化反应途径引起了广泛的兴趣。为了揭示非自由基活化机理,准确地判断催化剂中的活性位点是关键。目前科研工作者们普遍通过计算催化剂与过硫酸盐的吸附能(Eads)、PDS分子中的O-O键长(lO-O)或S-O键长(lS-O)等参数来判断催化剂中用于活化PDS的活性位点,然而这些判定标准并不能真实地反应非自由基活化过程中催化剂表面官能团对PDS的活化能力。因此,本文基于密度泛函理论计算(DFT)提出了一个新的描述符局部亲电指数(ω)用于描述吸附在催化剂表面的过硫酸根离子的氧化能力,将其与Eads、lO-O和lS-O综合考虑来准确鉴定以电荷转移机理为主的碳催化剂/过硫酸盐非自由基氧化体系中的活性位点。为了验证以上判定标准的有效性,我们比较了一系列有着不同物理化学性质的硼氮共掺杂的碳纳米管/纳米片(BCN-NT/NS)复合催化剂对PDS的活化性能。通过理论计算结合实验,证实了新的判定标准能准确判断催化剂中的活性位点,并且发现BCN-NT/NS的催化活化不仅与掺杂剂的浓度有关,且与B和N原子在碳骨架中的位置有关。这项工作不仅加深了基于电荷转移机理的过硫酸盐非自由基活化机制的理解,也为合理地设计高效的碳催化剂用于水处理提供了指导。
论文网址:https://doi.org/10.1039/D0EN00347F
论文下载:
Manuscript ID: D0EN00347F
Password: 516024
图表摘要:
论文英文摘要
Carbon-catalyzed persulfate activation is a metal-free advanced oxidation process for abating aqueous organic micropollutants. Recently, the electron-transfer mechanism in the activation of peroxydisulfate (PDS) has attracted tremendous interest due to its unknown nonradical reaction pathways. The conventionally used atomic-scale descriptors of adsorption energy (Eads), O–O bond length (lO–O) and S–O bond length (lS–O) cannot accurately reflect the ability of the functionalities of PDS in its activation. In this work, a new descriptor, local electrophilicity index (ω), which represents the oxidative capacity of adsorbed S2O82-, was included to identify the intrinsic active sites in carbocatalysts via density functional theory calculations. To verify the reliability of the proposed criteria, the catalytic performances of a series of highly boronated and nitrogenated carbon nanotube/nanosheet composites (BCN-NT/NS) with tailored physicochemical properties were comparatively studied for activating PDS to degrade phenol. By integrating the computational and experimental results, the catalytic activity of BCN-NT/NS was determined to not only be related to the contents of heteroatom dopants (B and N), but also the positions of B and N in the co-doping configurations. This study offers reliable criteria for determining the intrinsic catalytic sites in carbocatalysts for the activation of PDS based on an electron-transfer mechanism, which assists the rational design of nanocarbons as advanced catalysts for metal-free oxidation and water remediation.
资助项目
本研究受到国家自然科学基金(21806024,21777033,41415025),中国博士后科学基金(2017M622637),广东省科技计划项目(2017B020216003),广东省自然科学基金(2020A1515011150)及广东省本土创新团队项目(2017KCXTD012)的支持。